Arduino IDE
Essential Software for Arduino and ESP32 Boards
Arduino IDE is the software you’ll need to work with various microcontrollers, including popular ones like Arduino Uno, Arduino R3, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, and even the ESP32 Dev Board and ESP8266 boards, like the Expressif ESP32 Development Module or NodeMCU.
The Arduino IDE is your go-to tool for programming and developing projects with these compatible microcontroller boards.
With its user-friendly interface, you can easily write, compile, and upload code to unleash the full potential of these boards, including the ESP32. So, get ready to dive into the world of Arduino and ESP32 with this awesome software!

What is Arduino IDE used for?
Great question! Arduino IDE is like your personal software buddy for programming and developing projects with the Arduino Uno and other compatible boards. It’s super user-friendly and simplifies the process of writing, compiling, and uploading code to your Arduino R3, Esp32 dev board and other microcontrollers.
Think of it as your go-to tool for creating and editing sketches (aka programs) that make your microcontrollers come alive. It offers cool features like a code editor with syntax highlighting, a serial monitor for debugging and communication, and a library manager for easy integration of extra functionalities.
With Arduino IDE, you can unleash the full power of microcontrollers to control all sorts of electronic components—sensors, actuators, motors, displays, you name it! It’s a flexible and accessible environment that lets you prototype and bring to life innovative electronic projects, interactive installations, robotics, home automation, and so much more.
In a nutshell, Arduino IDE is your key to the exciting world of programming compatible microcontrollers and turning your ideas into reality. It’s your ticket to exploring and creating cool stuff in the electronics realm. Get ready to let your creativity soar and bring your projects to life with Arduino IDE!
How to Download the Arduino IDE?

How to Download the Arduino IDE?
To download the Arduino IDE, it’s super simple! All you have to do is follow these steps:
1. Open your web browser and go to the official Arduino website. 2. Look for the “Software” or “Downloads” section on the website. 3. Find the Arduino IDE download link for the Arduino IDE and click on it. 4. You’ll typically see different versions for various operating systems like Windows, macOS, or Linux. Choose the one that matches your system. 5. Once you’ve selected the right version, click on the download button. 6. Depending on your browser and settings, the file may automatically start downloading, or you might be prompted to choose a location to save the file. Pick a location you’ll remember, like your “Downloads” folder. 7. Wait for the download to complete. The file size is usually a few hundred megabytes, so it might take a little while depending on your internet speed. 8. Once the download is finished, locate the downloaded file in your chosen location. 9. If you downloaded a zip file, extract its contents by right-clicking on the file and selecting “Extract” or using a program like WinRAR or 7-Zip. 10. After extracting, you should see the Arduino IDE software ready to be used! Open the folder and run the application.
That’s it! You’ve successfully downloaded the Arduino IDE. Now you’re all set to start coding and creating amazing projects with your Arduino board. Enjoy the journey!

What are the main parts of the Arduino IDE?
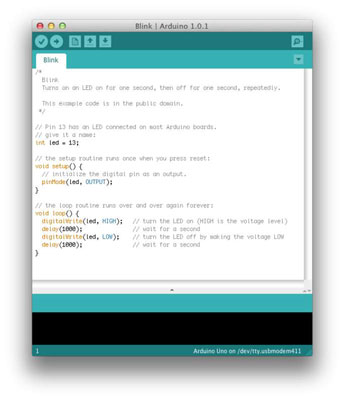
Welcome to the world of Arduino IDE! In this powerful development environment, you’ll find the Sketch Editor, Toolbar, and Serial Monitor to bring your Arduino projects to life.
Sketch Editor: The Sketch Editor is like your trusty digital notebook where you write your Arduino code. It’s the main area where the magic happens! You’ll find it right in the middle of the IDE. Here, you can write and edit your sketches using the Arduino programming language. It’s designed to make your coding experience easier with features like syntax highlighting (which color-codes different parts of your code), auto-indentation (which helps keep your code neatly organized), and code suggestions (which offer handy hints as you type). Think of the Sketch Editor as your creative canvas where you bring your ideas to life!
Toolbar: Think of the Toolbar as your command center within the Arduino IDE. It’s located at the top of the IDE, and it’s packed with helpful buttons for various actions. For example, you’ll find buttons to verify (or compile) your code to check for errors, upload your code to an Arduino board so it can run, open and save your sketches, and even open the Serial Monitor. The Toolbar is there to make your workflow smoother and more efficient, giving you quick access to essential functions.
Serial Monitor: Imagine having a conversation with your Arduino board—that’s where the Serial Monitor comes in! It’s like a chat window between you and your board. You can find it under the Tools menu. The Serial Monitor allows you to communicate with your Arduino board through the serial port. It displays messages that your board sends, and you can also send messages back to your board. This is incredibly useful for debugging and monitoring your code. You can use the Serial Monitor to receive data from sensors connected to your Arduino, print debug messages, or even control your project interactively. It’s like a window into the inner workings of your Arduino!
These three parts—the Sketch Editor, Toolbar, and Serial Monitor—are essential elements of the Arduino IDE that work together to make your Arduino programming experience enjoyable and efficient. The Sketch Editor is where you write your code, the Toolbar provides quick access to important functions, and the Serial Monitor allows you to communicate with your Arduino board, helping you understand what’s happening behind the scenes. So, grab your digital pen, explore the Toolbar, and open up the Serial Monitor to start creating amazing projects with Arduino!

Why is Arduino IDE called "integrated"?
Great question! The Arduino IDE is considered “integrated” because it brings together all the essential tools and features you need for programming and developing projects with Arduino boards in one cohesive software package. It’s like having a complete toolkit right at your fingertips!
When we say “integrated,” we mean that the Arduino IDE combines everything you need into a single program. It includes a code editor where you can write and edit your code files, a compiler that translates your code into a language the Arduino board can understand, and an uploader that sends your compiled code to the board.
But that’s not all! The Arduino IDE goes even further by providing additional features that make your programming experience smoother. It includes a serial monitor, which allows you to communicate with your Arduino board and monitor the data being sent or received. This is super handy for debugging and troubleshooting.
Moreover, the IDE integrates a library manager, which simplifies the process of adding extra functionalities to your projects. It lets you easily browse and install libraries developed by the Arduino community, saving you time and effort.
So, in a nutshell, the Arduino IDE is considered “integrated” because it combines all the necessary tools – code editor, compiler, uploader, serial monitor, and library manager – into a single software package. This integration streamlines the development process, making it easier and more convenient for you to write, compile, and upload code to your Arduino board. It’s like having a one-stop solution for all your Arduino programming needs!
Is the Arduino IDE C or C++?
Great question! Arduino IDE is primarily based on C++ programming language. It’s the language you’ll be using to write your code in the Arduino IDE software. So, when you’re creating sketches (programs) for your Arduino board, you’ll be working with C++.
The Arduino IDE software itself is designed to make it easier for you to code in C++. It provides a user-friendly interface where you can open, write, and edit your code files. The IDE also offers features like auto-completion and syntax highlighting to assist you while writing code.
To get started with Arduino IDE, you’ll need to download the software. Simply visit the official Arduino website, find the download section, and choose the appropriate version for your operating system. Once you’ve downloaded the Arduino IDE zip file, extract its contents and open the software.
With Arduino IDE, you can write your code in the integrated text editor, and when you’re ready, you can upload it to your Arduino board. The IDE takes care of compiling your code and uploading it to the board automatically. It’s a seamless process that makes programming your Arduino board a breeze.
Arduino IDE is compatible with a wide range of Arduino boards, so you can choose the one that suits your project requirements. The software supports various boards like Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, and more.
If you ever need assistance or want to explore more, Arduino has a vibrant community that provides support and resources. You can find helpful information, tutorials, and projects on the Arduino website and even on platforms like GitHub.
Remember to keep your Arduino IDE software up to date to benefit from the latest features, bug fixes, and security enhancements. Arduino releases new versions regularly, so it’s a good practice to download and install the latest version.
So, get ready to dive into the world of Arduino and start coding in C++ with the help of Arduino IDE. Have fun exploring and creating amazing projects with your Arduino board!
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Q. How to download the Arduino IDE?
A. You can download the Arduino IDE from the official Arduino website at www.arduino.cc. Navigate to the “Software” section, choose your operating system (Windows, Mac, or Linux), and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the download and installation.
Q. What is Arduino IDE used for?
A. Arduino IDE is used for writing, compiling, and uploading code to Arduino-compatible microcontroller boards. It provides an easy-to-use interface to program and develop projects with various Arduino boards, including the Arduino Uno, Mega, Nano, and ESP32.
Q. Is Arduino IDE C or C++?
A. Arduino IDE primarily uses a simplified version of C++ for programming. The environment combines the ease of C with some features of C++ to make it accessible for beginners while powerful enough for advanced users.
Q. Is Arduino IDE free?
A. Yes, Arduino IDE is free to download and use. It is open-source software, which means you can use, modify, and distribute it freely.
Q. Can Arduino IDE be used with Raspberry Pi?
A. Yes, the Arduino IDE can be installed and used on a Raspberry Pi. This allows you to program Arduino boards directly from your Raspberry Pi.
Q. Does Arduino IDE work on Mac?
A. Yes, Arduino IDE is compatible with Mac OS. You can download the Mac version from the Arduino website and install it on your Mac computer.
Q. Does Arduino IDE work on Chromebook?
A. The Arduino IDE does not natively support Chromebooks. However, you can use the Arduino Web Editor, which is a browser-based version of the IDE that works on Chromebooks.
Q. Does Arduino IDE work on iPad?
A. No, the Arduino IDE is not available for iPad. The software is designed for Windows, Mac, and Linux operating systems.
Q. Does Arduino IDE support ESP32?
A. Yes, Arduino IDE supports ESP32. You need to install the ESP32 board manager from the Board Manager within the IDE to start programming ESP32 boards.
Q. Is Arduino IDE a programming language?
A. No, Arduino IDE is not a programming language. It is an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) that supports programming languages, primarily a simplified version of C++.
Q. What is better than Arduino IDE?
A. The “best” IDE depends on your specific needs and preferences. Alternatives to Arduino IDE include PlatformIO, which offers more advanced features and supports multiple development platforms. Visual Studio Code with the Arduino extension is also popular for its powerful code editing and debugging features.