TokyMaker
What is TokyMaker?

Tokymaker is an innovative electronic prototyping tool designed for makers, educators, and students to create interactive projects with ease.
The drag-and-drop programming interface allows users to build logic and control components without writing code.
By simply connecting blocks in the visual editor, users can program actions such as turning on LEDs, controlling motors, and reading sensor data.
Easy to Learn – Block Coding
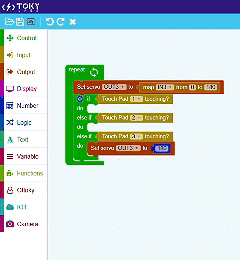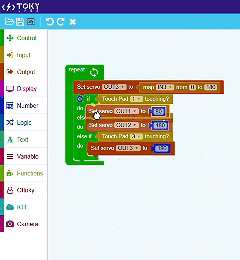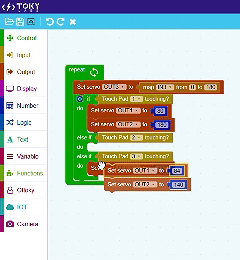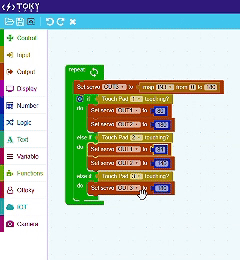
This approach eliminates the complexity of traditional coding, making it accessible for beginners while still offering flexibility for advanced projects.
With built-in sensors, Wi-Fi connectivity, and expandable inputs/outputs, Tokymaker empowers users to bring their ideas to life quickly and efficiently.
Introduction to Tokymaker
The TokyMaker IDE
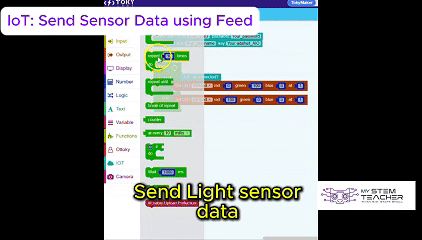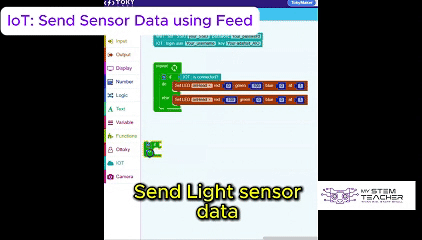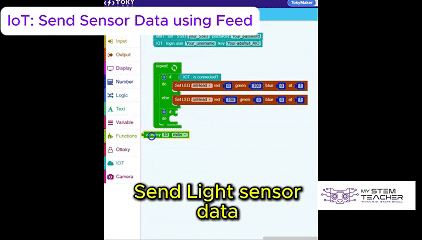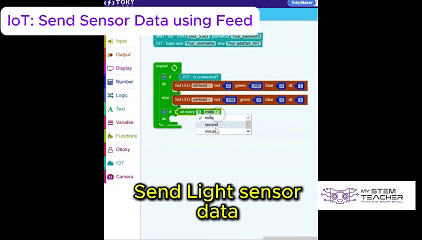
The Tokymaker Integrated Development Environment (IDE) provides a simple yet powerful way to program the device.
It supports both block-based visual coding and traditional JavaScript, making it accessible to beginners while offering flexibility for more advanced users.
The IDE allows seamless code deployment, real-time debugging, and cloud connectivity, ensuring a smooth development experience.
IoT (Internet of Things) projects
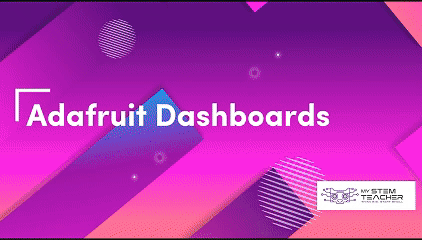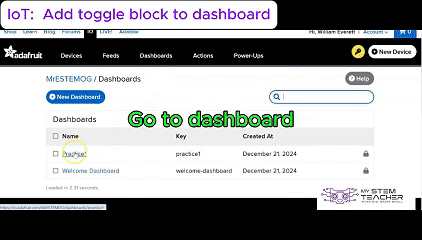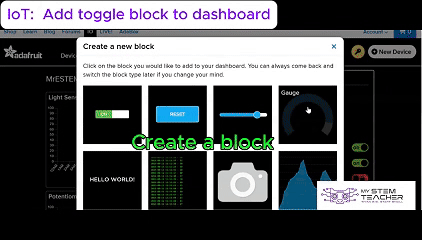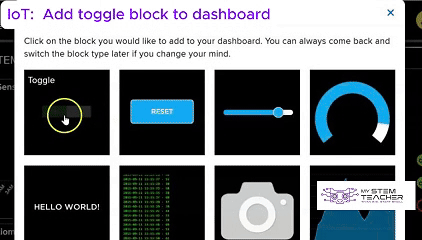
Tokymaker is an excellent platform for developing Internet of Things (IoT) projects, enabling seamless integration with services like IFTTT and Adafruit IO.
With built-in Wi-Fi connectivity, Tokymaker can send and receive data from the cloud, automate tasks, and interact with other smart devices.
Through IFTTT, users can create custom applets to trigger actions based on real-world events, such as sending notifications when a sensor detects movement.
Additionally, Adafruit IO allows for easy data visualization and cloud storage, making it simple to monitor and control IoT applications remotely.
Whether it’s home automation, smart monitoring systems, or cloud-based data logging, Tokymaker simplifies IoT development with an intuitive and powerful approach.
TokyMaker for Education
Tokymaker is widely used in STEM education to introduce students to electronics, programming, and IoT concepts. Its easy-to-use interface and hands-on learning approach make it an ideal tool for classrooms, workshops, and coding clubs. Students can experiment with real-world applications such as environmental monitoring, robotics, and smart devices, fostering creativity and problem-solving skills.

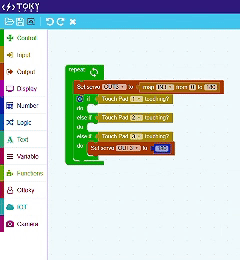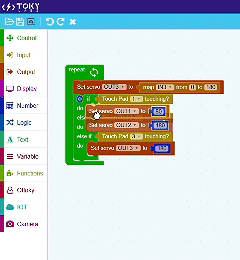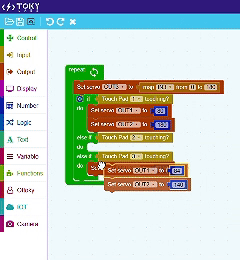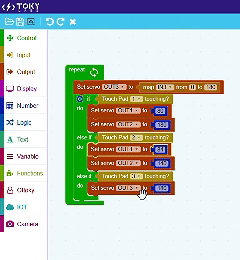
TokyMaker & Block Coding
Tokymaker simplifies programming with an intuitive block-based coding system powered by Google Blockly, making it ideal for beginners and educators. Instead of writing lines of code, users can drag and drop visual blocks to create logic and control their projects. This method helps users understand fundamental programming concepts like loops, conditions, and variables in a hands-on way. Since Blockly translates visual code into JavaScript, Tokymaker provides an easy transition from block coding to text-based programming. Whether you’re automating tasks, interacting with sensors, or integrating IoT services, Tokymaker’s Blockly-based environment makes coding both accessible and powerful.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Tokymaker FAQ
Q. What is Tokylabs?
Tokylabs is an educational technology company that designs hardware and software solutions for hands-on STEM learning. They focus on intuitive, beginner-friendly tools that help students and educators explore coding, electronics, and robotics without needing extensive prior knowledge.
Q. What is Tokymaker?
Tokymaker is a wireless, drag-and-drop programmable development board designed for STEM education. It allows users to create interactive projects using an easy-to-use interface, making it a great tool for beginners and young learners. It supports real-time programming via a web-based platform and is compatible with IoT applications.
Q. How do you code Tokymaker?
Tokymaker is programmed using a visual block-based coding environment similar to Google Blockly. Users can create logic-based programs by dragging and connecting blocks, making coding accessible for beginners. For advanced users, Tokymaker also supports JavaScript coding.
Q. Does Tokymaker require libraries?
No, Tokymaker does not require additional libraries. The platform provides built-in functionality, allowing users to access sensors, actuators, and connectivity features directly from the graphical programming interface or JavaScript editor.
Q. Is Tokymaker compatible with Arduino Uno sensors and actuators?
Yes, Tokymaker is compatible with many Arduino sensors and actuators. It has standard input and output ports that support components such as buttons, LEDs, temperature sensors, motors, and more. However, compatibility may vary depending on the specific sensor or module, so users may need to check wiring and signal requirements before integrating Arduino components.
Q. Can Tokymaker connect to the internet?
A. Yes, Tokymaker has built-in Wi-Fi capabilities, allowing it to connect to the internet for IoT (Internet of Things) applications. Users can send and receive data, interact with web services, and control projects remotely using cloud-based platforms.
Q. What power source does Tokymaker use?
A. Tokymaker can be powered via a micro-USB cable or a rechargeable lithium battery. This flexibility makes it suitable for both stationary and portable projects.
8. Can Tokymaker be used without a computer?
A. Yes, once a program is uploaded, Tokymaker can run autonomously without being connected to a computer. However, for coding and making changes, users will need access to a device with a web browser.
9. Is Tokymaker suitable for classroom use?
A. Absolutely! Tokymaker is designed for educational environments, from elementary schools to advanced STEM workshops. Its intuitive interface and hands-on approach make it ideal for teaching coding, electronics, and IoT concepts.
10. What are some example projects you can build with Tokymaker?
A. With Tokymaker, you can build projects such as:
Smart alarm systems (motion or light-based alerts)
Interactive games (touch-based or LED reaction games)
IoT home automation (Wi-Fi-controlled lights or appliances)
Weather stations (temperature and humidity monitoring)
Wearable tech (motion-based wristbands or accessories)